When you optimize your website, you want to base your decisions on correct data*. Spikes in your traffic might not always be payoff from good work… Even hidden deep down in your ordinary day-to-day traffic, lies spam traffic causing your site PAIN and making you take WRONG decision.
*Correct data = data generated from real users, using you site or app.
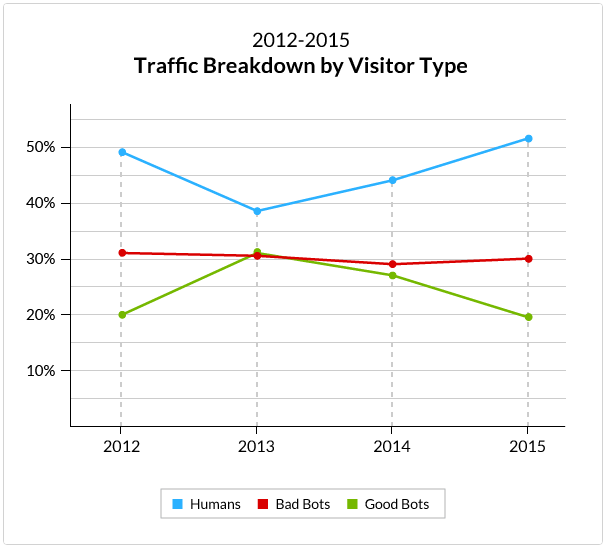
In 2015, real user traffic accounted for 52 % of all traffic on an average website, taking over bot traffic for the first time. However, the share of bot traffic (48 %) is still very large. This article looks at the effects of bot traffic on your analytics data and how you can make your data cleaner.
Hence, you deserve to make decisions based on observed user behaviour.
And, you deserve to prove your hypothesis on real users.
What is bot traffic?

Bots can then be separated into good and bad ones.
Good bots assist their owners with automated tasks such as data collection. They include, for example:
- Search engine bots crawling content on your website to index it (web spidering)
- Media bots giving updates on currency exchange rates, weather, sports and so on ().
Bad bots, on the other hand, are used for any type of malicious actions like
- Serving spam
- Searching and exploiting website vulnerabilities
- Stealing content and information
- DDoS attacks (attempt to take down your server completely by overwhelming it)
There are two main types of bad bot traffic you can find in your Google Analytics reports.
Zombie spam bots
Zombie spam bots crawl the web and visit the sites executing the Google Analytics script in the process. With the hit these bots send fraudulent referrer headers containing the website URL that they want to promote. This type of traffic appears both in Google Analytics and in your server logs, so you can block zombie spam bots on the server side as well.
Ghost referrer spam
As opposed to the zombie spam bots, ghost referrer bots do not actually visit your website, instead they connect to the Google Analytics servers directly through Measurement protocol with your GA property ID. Ghost referrer spam can be seen in Google Analytics reports, but not in server logs.
Spammers can access your property ID in one of two ways:
- By scrapping IDs from visited pages if your Google Analytics tracking code is hard-coded on the website, or
- By targeting random property IDs. In that case the spammer does not know what website refers to a particular property ID, so that ghost spam appears with fraudulent hostnames and page titles in GA reports.
Since ghost referrer traffic does not show in your server logs, you can block this type of spam only in Google Analytics.
Why should I filter away bad bot traffic?
Basically: They affect your data, and will modify the “truth” about about your users. Meaning, the data you see in your analytics tool is not a reflection of real users behaviour.
Bot traffic can sabotage some of your key performance metrics, like session count, engagement and conversion rates. Without filtering away bad bot traffic, you will see artificially pumped incoming traffic, higher bounce rates, shorter visit duration and lower conversion rate.
Relying on inaccurate data may lead you to making bad decisions for your business.
Another problem with bot traffic is that it increases load on your servers. An overloaded server in turn means longer page load times for the visitors to your website negatively affecting users’ experience.
How come bots can affect my data in the first place?
More and more bots execute JavaScript on your website and thus will appear as hits in GA. This is the type of traffic you should consider taking some action on, since they appear as “users”
Bots used by most search engines, and some basic bad bots, will not show up in your Google Analytics reports because they do not run JavaScript on your website. These hits will show up only in your server logs and have no effect on the analytics data.
1/3 of your traffic might be spam
Bad bot traffic is usually low quality and can negatively affect your aggregate analytics data. While the amount of bot traffic varies with the size of a website, smaller websites are more likely to be visited by both good and bad bots. Even larger websites that commonly have higher security and traffic filtration can have almost a third of overall traffic coming from bad bots.
However, bad bot traffic have a greater impact on analytics data for small and medium websites. Bad bots visit small and medium websites at least as often as humans do. The ratio is even larger for small websites (see the graph below).
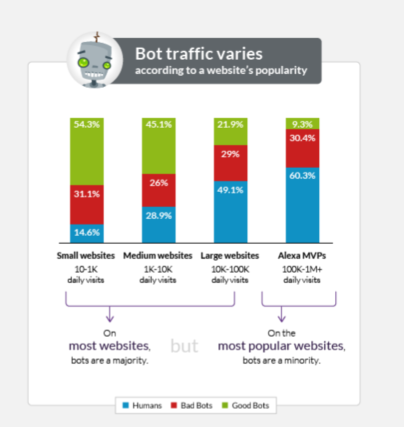
How to detect bad bot traffic in Google Analytics
In several reports in Google Analytics (we list them later on) you should look for a combination of characteristics that can help you identify bot traffic:
- Very low average session duration
- Page depth averages one to two pages a session
- Near 100% (or 0%) bounce rate
- Share of new sessions is around 100% or 0%.
- No goal completions or e-commerce transactions associated with the traffic
- Some referrers simply have suspiciously looking names.
If you have received referral traffic from a website you don’t recognize or don’t expect to receive traffic from, do NOT visit that referring site. Do a quick online search first, to see whether you can trust the source. Otherwise you bring more traffic to the spammer’s website and, at worst, risk getting a virus on your computer.
However, bots are becoming smarter and more sophisticated. According to Imperva Incapsula’s 2015-2016 Annual Global DDoS Threat Landscape report, the number of bots able to bypass at least some of the security tests rose to record high 36.6% in Q1 2016. Broken down, 18.9 percent of bots were able to accept and hold cookies and the other 17.7 percent were also able to parse JavaScript.
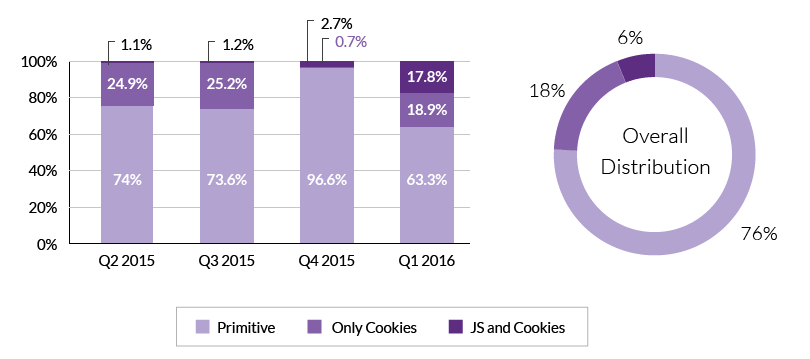
Where to look for bad bot traffic
There are a few reports in Google Analytics you should check to see how spam affects your website traffic.
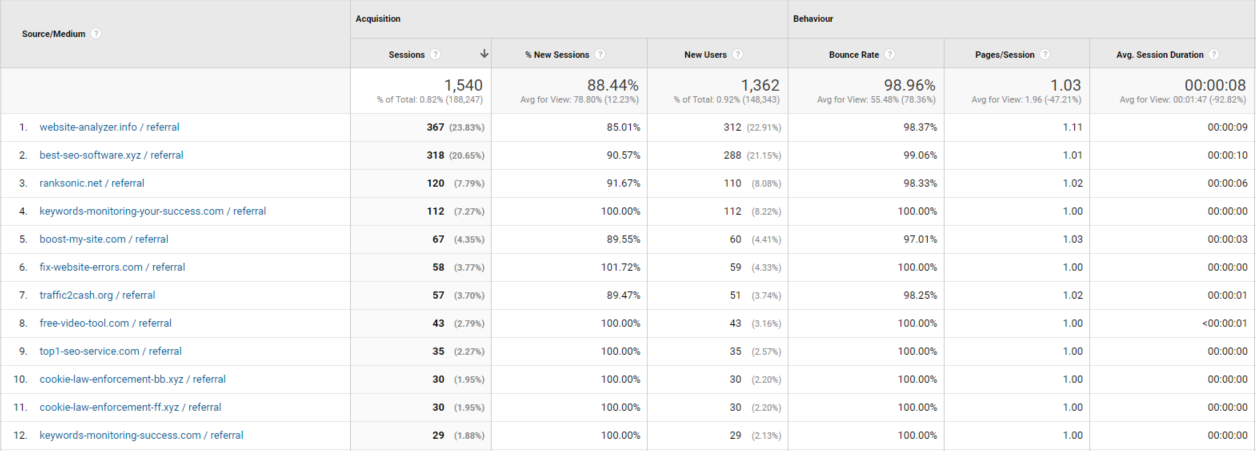
Referrals & Source/Medium
The main reports where you can see spam referral traffic are: Referrals report and Source/Medium report. You can access them both by going to Acquisition > All Traffic.
However, some of the spam traffic can appear even as fake pageviews, events and direct visits.
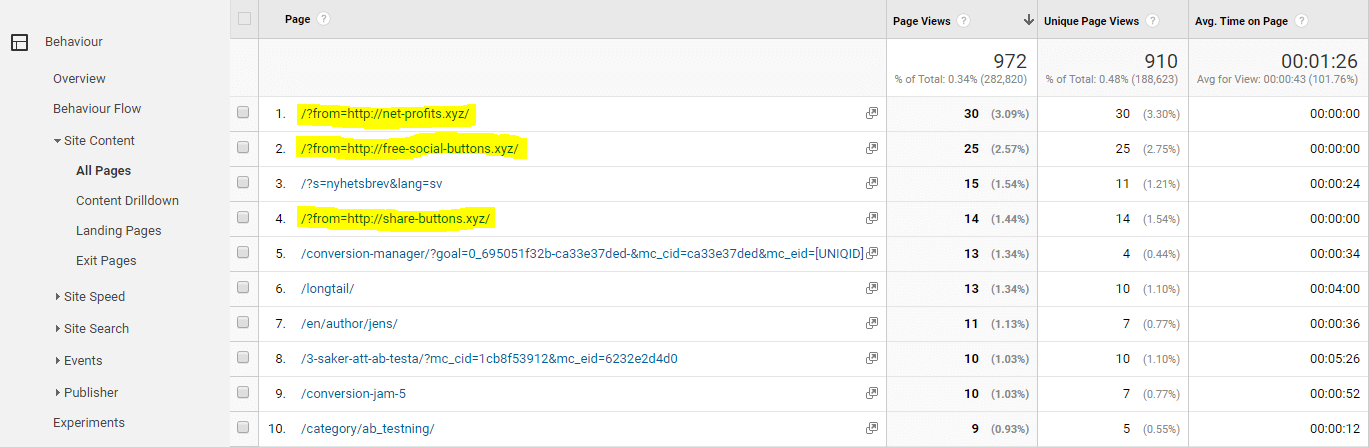
Fake pageviews
Fraudulent pageviews appearing in All Pages report are URLs that do not exist on your website. Instead, these pages contain URLs that spam bots want you to visit.
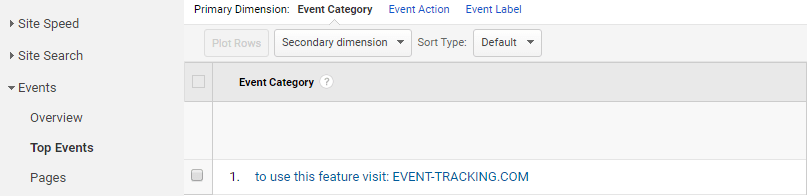
Fake events
You can also find referrer spam among event categories as well (see an example extract from Top Events report below). Such events do not actually take place on you website and are visible only in Google Analytics.
Direct visits
Some spam bots do not send referrer headers with a hit. Such traffic would appear as direct traffic in your Google Analytics reports instead, making it even more difficult to detect.
You can also find bot footprints in the Technology reports found under Audience, like overrepresented but usually unusual service providers (more about that further down).
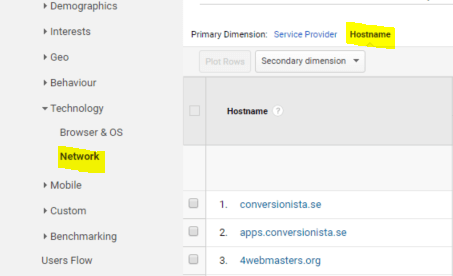
Network report
In the Network report you should look for service providers that bring in low quality traffic. A number of internet service providers, such as google inc, microsoft corporation and inktomi corporation, tend to generate huge bot traffic.
Don’t be surprised to find apparent bot traffic from service providers like Google and Microsoft. Bots simply run via their respective cloud servers in an attempt to disguise themselves.
Browser & OS report
The Browser & OS report can help you find browser versions that skew your data. Sizable, high-bounce traffic from very outdated browser versions can be an indication of spam traffic.
Often you have to look for a specific combination of browser, browser version, screen resolution and Internet service provider that comes during specific hours of the day to identify bots.
How to filter out bot statistics in my Google Analytics data
After you have determined how your Google Analytics data is affected by bad bot traffic, it is time to address the issue. There is no universal solution to filter away bot traffic completely, but you can take a few steps to clean up your analytics data.
These steps include creating a number of filters.
We suggest that you test these filters in a separate test view before applying them on your main data, because filters are destructive. Anything you exclude will be gone forever. You should not use the filters in the unfiltered view in your property either, so that you always have access to raw, unmodified data in case of an error.
1 Exclude known bots
Check the box Exclude all hits from known bots and spiders under View settings inside the Admin section

The checkbox is located towards the bottom of the View settings list. You should check this box on every view where you want to filter bots and spiders.
2 Filtering ghost bot traffic
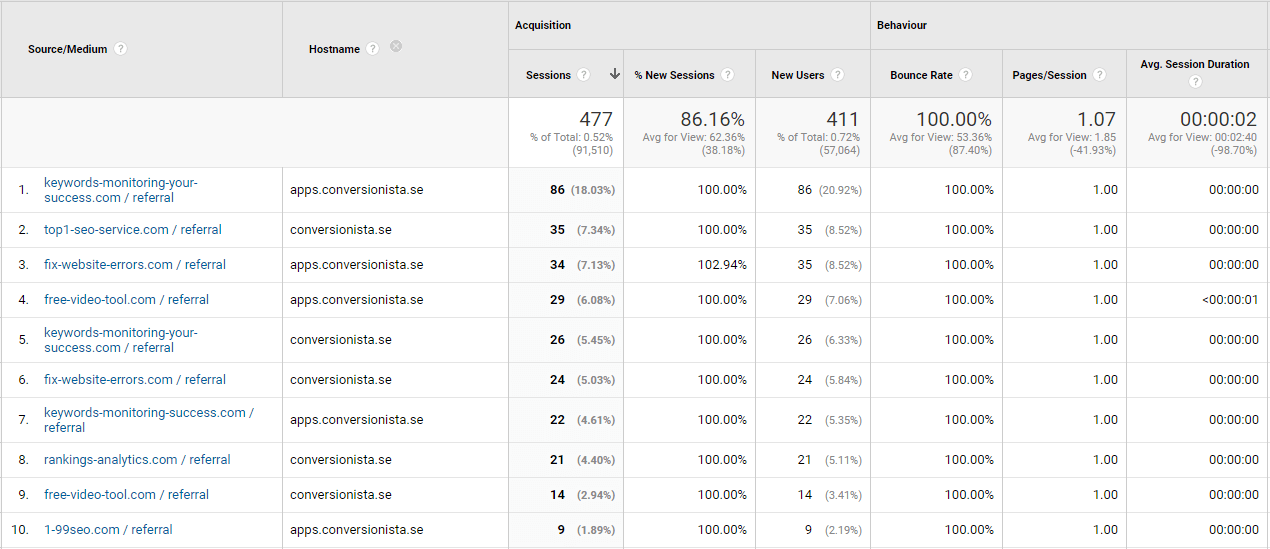
- Since this type of spam traffic does not show up to your server, one way to filter it is to implement a Hostname filter in GA. First, you should identify valid hostnames for your website. To do that navigate to the Network report (Audience > Technology > Network) and choose Hostname as primary dimension.
- Specify your date range as far back as possible.
- In the report identify legitimate hostnames that are related to your website. In out case, an example of a valid hostname will be conversionista.se. Everything else, including (not set), is most probably spam.
- Create a regular expression (regex) to include only domains you consider to be valid. It will suffice to specify only the root domain, as regex will perform a match on all subdomains by default.
- Under the Admin tab, choose Filters in the View column. Remember to choose the correct View to apply your filter to.
- Add a new custom filter, select Include and Hostname in Filter field. Then add the regex with valid hostnames you created into the Filter Pattern field
- Save your filter
3 Filtering zombie spam visits
The valid hostname filter will not keep the spammers that set the hostname to your own or actually visit your website.
So you need to exclude such visits with a separate Referral spam filter. This filter is based on Campaign Source and a regex that includes the referral spam domains.
Using Referral in the Filter Field will not always work, because some spammers set the value into the Campaign source field instead.
This filter will require constant update with the discovery of more spam referrals. You may even need to create more than one such filter because the Filter pattern field has a limit to the number of characters. Be careful with your expressions and always test your filters, as they exclude all the traffic that matches the pattern. You can also use Spam Filter Insertion Tool that Simo Ahava has created to exclude spam referrals. A more detailed description of this tool can be found here.
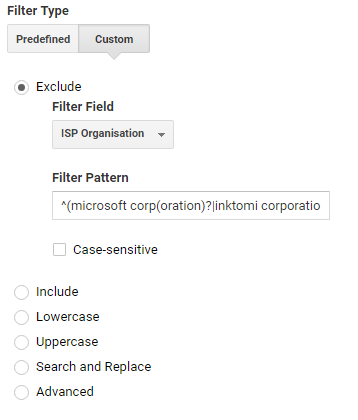
4 Filtering Service Providers
If you have identified particular Service Providers that are responsible for spam traffic, you can create a filter excluding them from your data. Such a filter should exclude ISP Organisation matching a regex pattern with spam Service Providers you have identified in your GA Network report.
5 Create an advanced segment
Since filters cannot be applied retroactively, you should use custom segments to analyse your historical data. This advanced segment should combine the Hostname, Referral and any other spam exclusion filters that you created in the earlier steps.
Keep the following in mind
Do not use the Referral Exclusion List
By default, a referral automatically triggers a new session. Referral exclusions prevent traffic that arrives to your site from the excluded referral source from starting a new session.
Common uses of referral exclusion lists include third-party payment processors and cross-subdomain tracking. When you receive a visit from a spam referrer added to the referral exclusion list, Google will still report a visit but strip the referral information off in the process. Since the referring source has been set to be ignored, these visits will be marked as Direct traffic instead. So even though the spam referral traffic has disappeared, you will still see inaccurate data in your GA reports.
Server-side technical solutions wont filter all bots
Using .htaccess rules or WordPress plugins will not eliminate any of the ghost referrals. Since ghost bot traffic does not interact with the server, server-side technical solutions will not make your analytics data cleaner.
Keep your data fresh and clean and always be converting! And always ask questions if you have any (below).